Laboratory: Making a Speaker
by
Regan Lum
Introduction:
A speaker is a device that converts an electronic signal into
sound. The speaker you will build (see figure 1) consists of a Styrofoam or
paper cup, a coil of wire, a permanent magnet, and a signal source. The
electronic signal goes through the coil and creates a varying electromagnet.
The attraction and repulsion between the electromagnet and the permanent
magnet cause the cup to vibrate and produce sound.
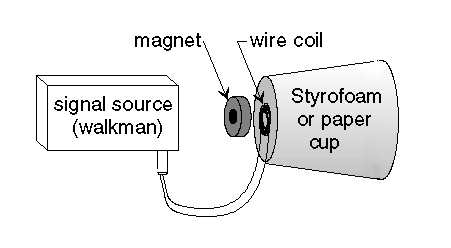 figure 1
figure 1
Purpose:
In this laboratory, you will explore how a speaker works.
Materials:
- 1 permanent magnet
- 2 feet of wire
- 1 pencil
- tape or glue
- 1 Styrofoam or paper cup
- 1 signal source (tape player)
- 1 plug with alligator clips for tape player
Procedure:
Assemble material as shown in figure 1.
- Leaving about 10 centimeters on the end, wrap the wire around a pencil to
make a wire coil and tape or glue it to the bottom of the cup. The coil
should be about 1 centimeter in diameter and contain about 15 coils.
- Strip the insulation off the ends of the wire.
- Place the magnet on the wire coil.
- Connect the signal source (tape player).
- Adjust the apparatus until you get sound coming out of your speaker.
Conclusion
- Does the volume control on the tape player work on your speaker?
- What kind of sound quality do you get out of your speaker? Compare the loudness and the clarity.
- How does the sound quality compare with your string walkie talkie?
- Explain how your speaker reproduce sound.
For more information, email your comments to
outreach@cea.berkeley.edu
or contact
Regan Lum
All text, images, and other resources in this
page are Copyright © 1995, The Regents of the University of California. All rights reserved.
For permission, email outreach@cea.berkeley.edu.
 Return
to CEA Science Education Home Page
Return
to CEA Science Education Home Page
 figure 1
figure 1
 figure 1
figure 1