 |
| A rare red
aurora as seen from Fairbanks, Alaska. Photograph
©Jan Curtis |
|
The most spectacular manifestation of the
connection between the Sun and the Earth is the Aurora Borealis
(Northern Lights) and the Aurora Australis (Southern Lights).
For millennia, people have watched them and worried about
what ill portents they were heralding. It wasn't until the
mid-1800s that scientific studies began to uncover many of
their mysteries.
Magnetic Storms
Scientists learned that aurora often
accompanied magnetic 'storms' and an unsettled magnetosphere;
they were produced by flows of charged particles entering
the atmosphere; they came and went with the sunspot cycle;
and their colors were the product of excited oxygen and nitrogen
atoms about a hundred miles above the surface of the Earth.
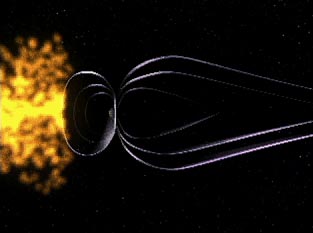 |
| This
NASA animation shows the Sun interacting with
the Earth's magnetosphere causing auroras.
(Click
to launch movie.)
|
|
|
By the turn of the 20th century, scientists
actually created artificial aurora in their laboratories,
and once television and the fluorescent lamp were invented,
it became pretty clear just how auroras could be created by
electrons hitting the gas in the atmosphere. These collisions
would cause atoms of oxygen and nitrogen to fluoresce and
produce the characteristic colors of red, blue and green.
What scientists still didn't understand was where the electrons
came from. Some thought it was direct currents of particles
from the Sun itself. Others felt it was more complicated than
that.
What we have learned from direct satellite studies
in the 1970s is that these flows of particles definitely do
not come from the Sun. Despite what many simplified accounts
might suggest, auroras are not caused by the direct flow of
particles from the Sun into the polar regions, guided by Earth's
magnetic fields. Instead, these currents are generated in
the distant, comet-like tail of Earth's magnetosphere, whenever
solar activity and severe solar storms are in progress. During
a solar storm, some of the energy stored in the tail of the
Earth's magnetic field is transformed into high-speed currents
of charged particles.
Charged Particles
These accelerated particles flow
into the equatorial regions of near-Earth space and become
trapped as the ring current. Positively charged particles
drift westward while negatively charged particles drift eastward.
In a process scientists don't fully understand, some of these
particles also flow along the magnetic field into the polar
regions. As they enter the upper atmosphere they are accelerated
to even higher energies before colliding with atoms of oxygen
and nitrogen to produce the aurora's colors. These million-ampere
currents not only cause the spectacular displays we see as
aurora, but they also heat the upper atmosphere and ionosphere.
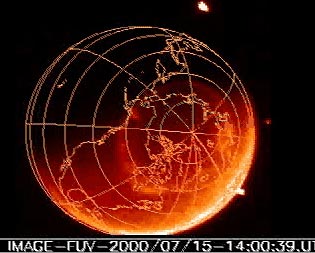 |
| Ultraviolet
images of the aurora from space. Taken by
the Far Ultraviolet Imager (FUV).
(Click
to launch movie.)
|
|
|
 Find out more about the Sun-Earth Connection at the Sun-Earth
Connection Education Forum Web site.
Find out more about the Sun-Earth Connection at the Sun-Earth
Connection Education Forum Web site.
Text adapted from the
Sun-Earth Connection Tutorial courtesy of NASA, originally
written by Dr. Sten Odenwald. Images and videos courtesy of
NASA unless otherwised noted.
|