
Torrential rains that accompany the
monsoon can cause widespread flooding as seen in this aerial photo.
|
|
|
|
For
thousands of years Indian farmers sweated through spring and
early summer, watching for that climactic moment when the monsoon
rains broke. An enormous folk literature surrounds the unpredictable
monsoon, including doggerel and proverbs about the formation
of nimbus clouds, the arrival of migrant birds, and subtle
changes
in
vegetation. The pied crested cuckoo is said to arrive on the
west coast a day or two before the rains, fly inland at a leisurely
pace, and then appear in Delhi about two weeks after the monsoon
breaks over the Western Ghat Mountains inshore from the coast.
| |
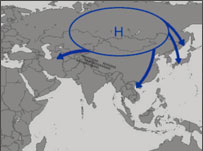
| This movie briefly
explains how the monsoon works.
Movie courtesy NASA Data Assimilation
Office. |
|
|
The word monsoon comes from the Arabic word mausem
(season). The monsoon is a season of rains borne
on the dark nimbus clouds
of summer that blow in from the southwest. A huge circulation
of air determines the intensity of the monsoon. As the Earth’s
tilt varies with summer and winter, so the monsoon circulation
moves—further north in summer, southward in winter. In
summer the northern edge of the monsoon borders on the Himalayas.
Winds blow across the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal, bringing
moisture-laden air to Sri Lanka in May, and to the southernmost
parts of peninsular India by the first week of June. The rains
move steadily northward to Bombay. By mid-June they normally
cover all of Gujerat, with heavy rain along the west coast
and the shores of the Bay of Bengal. In a good monsoon year,
rain showers continue throughout western India and Pakistan
through September, and less certainly, from the southward-retreating
monsoon into November. The agricultural lives of millions of
village farmers depend on this pattern of circulation from
south to north and back again. If the pattern fails, less moisture,
sometimes almost none, reaches the Punjab or Rajasthan. Farther
south, the usually strong southwestern monsoon winds blow with
less force and drop scanty rainfall inland. Even in good years,
irregular rainfall patterns can play havoc with crops of all
kinds.
Page 2 of 3 |
|
|




