Constellations
A constellation is an apparent grouping of bright stars in the night sky. The groupings are highly dependent on who is observing them.Currently, the International Astronomical Union (IAU) divides the sky into 88 regions it recognizes as Constellations.
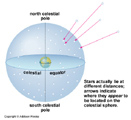
Stars in a Constellation are all in the same direction of the sky, but may not be physically close to one another in space. Stars so far away that there is no sense of depth in the sky. Everything appears as if it were on a sphere surrounding Earth. We call this imaginary sphere the Celestial Sphere.
Finding Your way around the Sky:
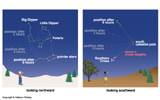 The Big and Little Dipper. The North Celestial Pole -- The North Star: Polaris -- A star directly above the North Pole of Earth. A location called the North Celestial Pole.
The Big and Little Dipper. The North Celestial Pole -- The North Star: Polaris -- A star directly above the North Pole of Earth. A location called the North Celestial Pole.
- Follow the Arc to Arcturus (Bootes), drive a Spike to Spica (Virgo)
- The Ecliptic: Plane of Earth's Orbit around the Sun. All planets and the Moon are found near this plane. Solar System is a thin disk. Planets all orbit the Sun in roughly the same plane.
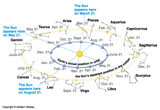 The Zodiac: Group of Constellations through which the Sun passes during the year. Constellations in the ecliptic plane. 13 IAU recognized constellations in the Zodiac.
The Zodiac: Group of Constellations through which the Sun passes during the year. Constellations in the ecliptic plane. 13 IAU recognized constellations in the Zodiac.
Horizons and Local Coordinate Systems
When describing where to look for Astronomical Objects to others, one must use a Coordinate System. A Local Coordinate systems works well for making observations from any location on Earth.Begin with Compass Directions: North, East, South, and West
- East is the Direction in which the Earth spins.
- Use a Right Hand Rule to find North relative to East.
- West is opposite East
- South is opposite North
- 2D-coordinate system
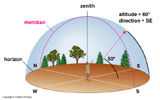
- Zenith: The point in the sky directly above your head. A line from the Center of Earth to your location on the surface points to the Zenith in the sky.
- Horizon: Where the Sky Meets the Earth. Place at which you can see no further. At surface of the Earth the Horizon is 90° from the Zenith.
- Meridian: Line (arc) through the sky connecting North and South and diving the Sky into an East and West side.
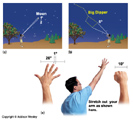
Use Angles to measure locations of objects relative to one another.- Altitude: The angle above the horizon at the Surface of Earth.
- Use two pieces of info to locate objects in local sky. Compass Direction, and Altitude.
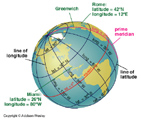
Finding Compass Directions:
- Use a magnetic compass -- not accurate because magnetic poles not aligned with geographic poles.
- Use North Star to locate North.
- Use a map to locate Compass Directions.

Diurnal Motions
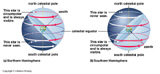
Because the Earth Spins West to East. The Sky appears to rotate about us East to West. Objects rise in the East and Set in the West. All astronomical objects follow this daily motion.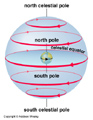
Portion of sky seen and daily motion of stars depends on one's location on Earth.
Stars within a certain angular radius of the North or South Celestial Poles (equal to the latitude on Earth) never rise or set but circle the poles. These stars are said to be Cirumpolar
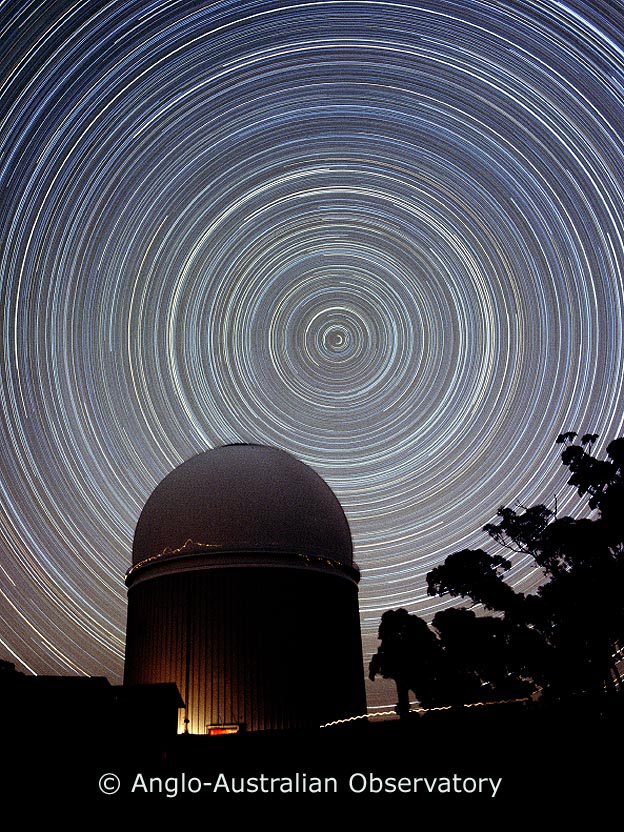

Seasonal Motions
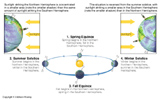
As the Earth revovles about the Sun the Constellations visible at night change. Due to the tilt of Earth's rotation axis relative to it's orbital plane the Sun appears to change its location on the horizon where it rises and sets throughout the year.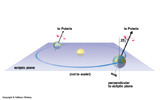
Cause of the Seasons
Earth's Seasons Are Caused by the Axial Tilt! No Tilt, No Seasons.- Solstices: Locations in Earth's orbit when the axis is pointed the most toward or away from the Sun. The longest and shortest day of the year depending on which hemisphere you live, North or South.
- Equinoxes: Locations in Earth's orbit when the axis is not pointed at all toward or away from the Sun, but tangent to it. Length of the day is the same for everyone on Earth. 12 hours of day and 12 hours of night.
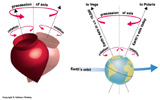
Earth's rotation axis Precesses about in a 26,000 year cycle. This Changes the Date of Equinoxes and Solstices.
Seasons happen because sunlight is distributed over the surface of Earth differently throughout the year, NOT because the Earth is closer or farther away.
When Sunlight is direct is delivers more energy per unit surface area than when it is indirect (or oblique).
Tilt also causes length of days to change. During summer, days are longer and sunlight is more direct. During winter, days are short and sunlight is more oblique.
Return to Class Notes Page